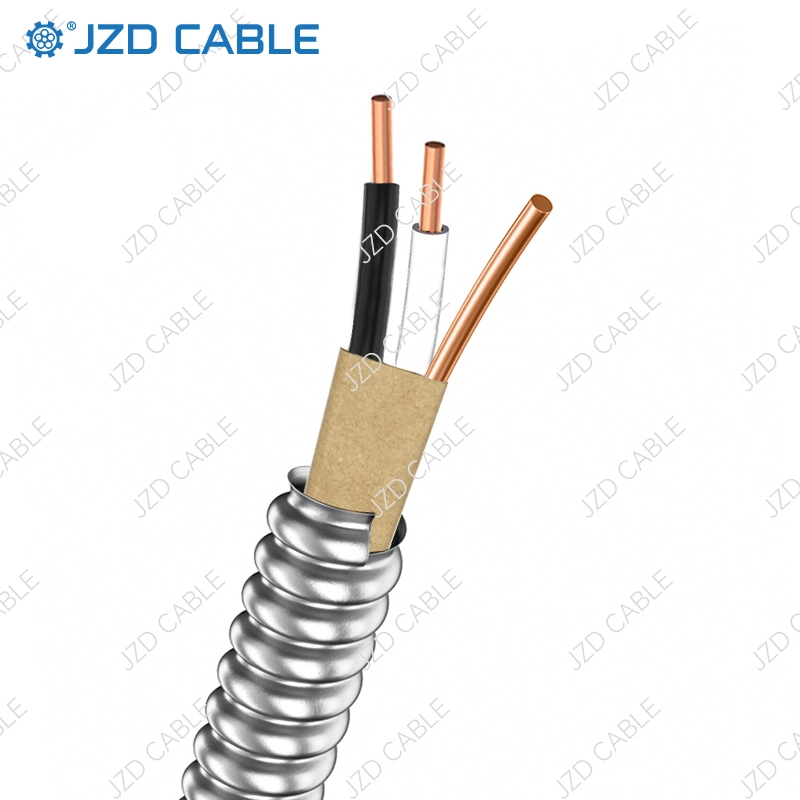
What is Nylon Cable?

Features and Applications of Nylon Cable
- Abrasion Resistance: High surface hardness and low friction coefficient protect against wear during installation and dragging, extending service life.
- Impact Toughness: Withstands mechanical stress such as squeezing and collisions, safeguarding internal conductors and insulation.
- High Strength and Flexibility: Superior tensile and tear resistance, with materials like PA12 offering flexibility for bending applications.
2.Strong Chemical Resistance
- Resistant to oils, fuels, solvents, and cleaning agents, making it ideal for chemical plants and engineering machinery exposed to corrosive substances.
- Operates reliably in temperatures from -40°C to 90°C, meeting demands for high-temperature environments.
- Halogen-Free: Produced without halogen additives, reducing smoke and toxicity during combustion. Complies with ROHS standards.
- Flame Retardancy: Self-extinguishing properties; can meet UL VW-1 and IEC 60332 standards with additives, suitable for construction and rail transit.
- Lightweight: Small outer diameter and low weight with a minimal static friction coefficient for easy installation.
- Ease of Processing: Allows thin-wall extrusion for uniform sheathing and cost efficiency.

Typical Applications
- Ideal for in-building conduit wiring due to its smooth surface and small diameter, reducing friction and insulation damage. Suitable for highway monitoring equipment and lighting systems.
- Perfect for high-stress environments like robotic and drag chain cables, offering abrasion and impact resistance in automation and machinery.
3.Automotive and Aerospace:
- Automotive Wiring: Resistant to oil and high temperatures (up to 150°C short-term), used in engine compartments and braking systems. Its lightweight nature helps reduce vehicle weight.
- Aerospace Systems: Applied in low-voltage aircraft wiring, offering chemical corrosion resistance and cold resistance (-40°C).
- Used in connectors, switches, and sockets for its insulation and heat resistance. Especially suitable for flame-retardant (e.g., UL-certified THHN cables) or anti-static applications.
- Resistant to rodents, chemicals, acids, and alkalis, making it suitable for high-risk environments like petrochemical plants and underground installations.
Common Mistakes in Selecting Nylon Cable
-
Incorrect conductor size or voltage rating. -
Improper installation methods, leading to insulation damage. -
Ignoring environmental factors like temperature and chemical exposure. -
Using low-quality cables to save costs, risking failures. -
Overlooking certifications like UL, CE, or TUV, which may lead to non-compliance or safety hazards.
Tips for Optimal Selection
-
Evaluate environmental conditions, mechanical needs, and electrical requirements. -
Verify certification compliance and ensure cables meet project-specific parameters.