Selecting the correct type of electrical cable is a fundamental step in any construction or renovation project. Safety, compliance, and performance all hinge on this critical choice. Among the various options, NMD-90 and NM-B wires are two of the most commonly specified types for residential and commercial building wiring. While they share similarities, understanding their key differences is essential for proper application. This guide will clarify what each cable is, compare their features, and help you decide which one is right for your needs.
What is NMD-90 Wire?
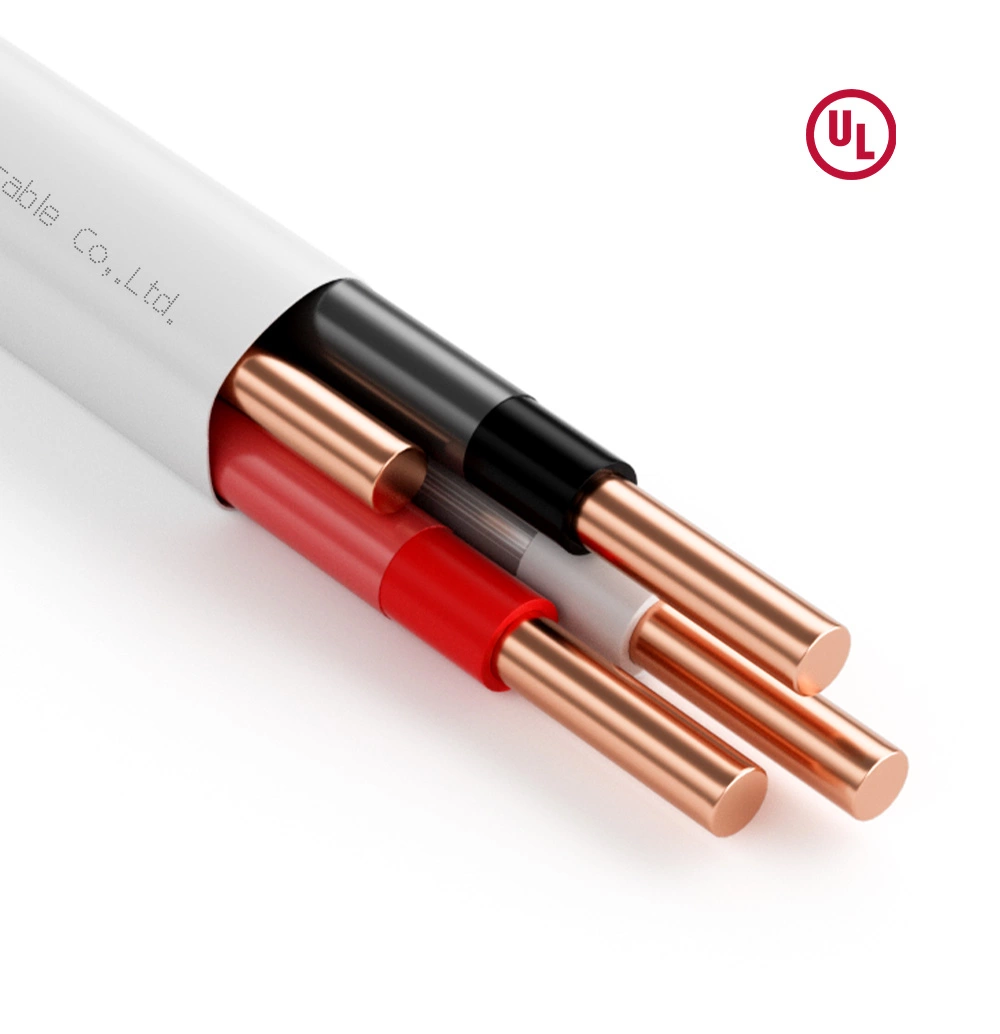
NMD-90 stands for Non-Metallic Dry 90°C. It is a Canadian Standards Association (CSA)-approved cable primarily used in Canada. The “90” denotes its maximum conductor temperature rating of 90°C. This cable is designed for use in dry locations within buildings, such as inside walls, floors, and ceilings. A key feature of NMD-90 is its triple-layer protection: individual insulated conductors are wrapped in a paper binder, then protected by an overall flame-retardant, moisture-resistant PVC jacket. It typically contains a bare copper ground wire alongside the insulated current-carrying conductors (e.g., black, red, white).
What is NM-B Wire?
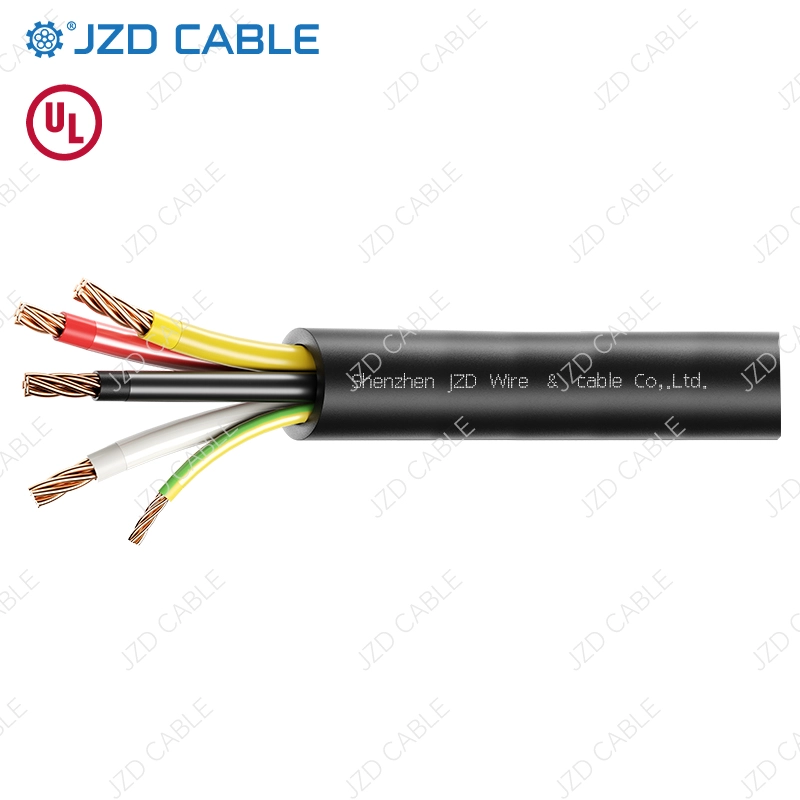
NM-B stands for Non-Metallic Building wire, with the “B” indicating a maximum conductor temperature rating of 90°C. It is the standard under the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States, often referred to by the common brand name “Romex.” Like NMD-90, NM-B is intended for dry, interior locations in residential and commercial construction. It consists of two or more insulated conductors and a bare ground wire, all enclosed within a non-metallic, flame-retardant outer jacket. It is the go-to cable for most indoor branch circuit wiring in the U.S.
Key Similarities Between NMD-90 and NM-B Wire
Despite their different governing standards, these cables serve a very similar primary purpose and share several important characteristics:
- Application: Both are used for dry, interior wiring in residential and light commercial buildings (e.g., outlets, switches, lighting).
- Temperature Rating: Both have a maximum 90°C conductor rating, though their ampacity (current-carrying capacity) is typically based on the 60°C or 75°C column of code tables to account for termination ratings.
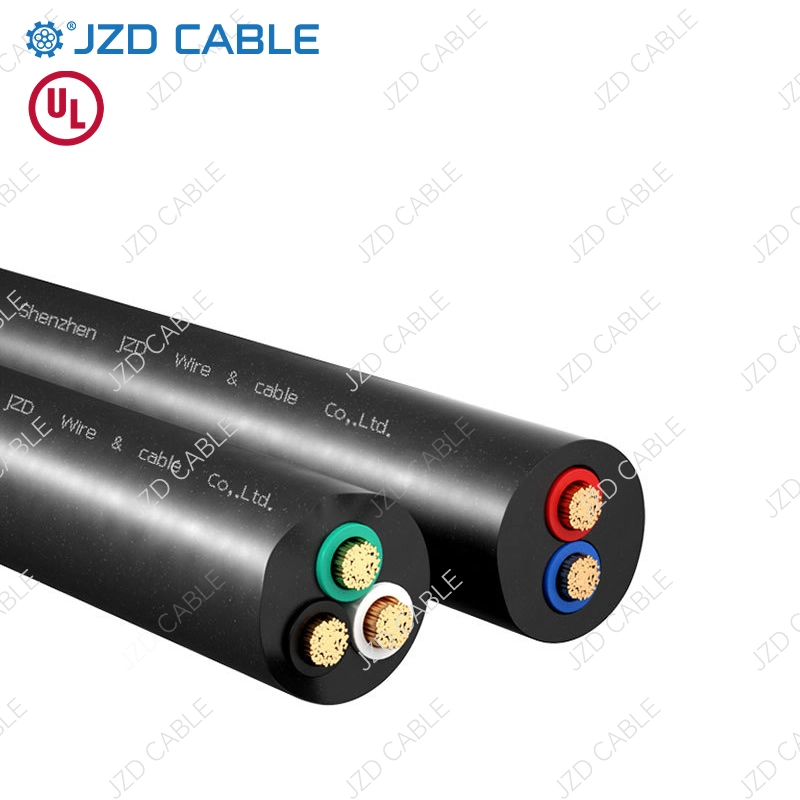
- Basic Construction: Both consist of insulated copper conductors (solid or stranded) and a bare equipment grounding conductor, all housed within an overall non-metallic jacket.
- Conductor Material: Both are almost exclusively available with copper conductors.
Key Differences Between NMD-90 and NM-B Wire
The main differences lie in their standards, specific construction details, and regional usage.
|
Feature
|
NMD-90 Wire
|
NM-B Wire
|
|---|---|---|
|
Governing Standard
|
Canadian Standards Association (CSA) C22.2 No. 75
|
National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S. (UL Standard 719)
|
|
Primary Market
|
Canada
|
United States
|
|
Outer Jacket
|
Flame-retardant, moisture-resistant PVC. Often includes a paper binder layer between conductors and jacket for added protection and stripability.
|
Flame-retardant, moisture-resistant PVC. Does not typically include an internal paper wrap.
|
|
Common Sizes & Configurations
|
Widely available in a broad range (e.g., 14/2, 12/2, 10/2, 14/3, 12/3).
|
Widely available in a broad range (e.g., 14/2, 12/2, 10/2, 14/3, 12/3).
|
|
Color Coding
|
The outer jacket is often white for standard sizes, but other colors may indicate specific applications or sizes.
|
The outer jacket is color-coded by wire gauge: White (14 AWG), Yellow (12 AWG), Orange (10 AWG), Black (8 AWG & 6 AWG).
|
|
Labeling/Marking
|
Must be marked with “NMD90” and CSA certification mark.
|
Must be marked with “NM-B,” wire gauge, conductor count, and UL or ETL listing mark.
|
How to Choose the Right Wire: NMD-90 or NM-B?
Your choice is primarily dictated by location and electrical code compliance.
- Follow Local Codes: This is the most critical rule. If your project is in Canada, you must use CSA-approved NMD-90 cable (or other approved Canadian types like NMWU for wet locations). For projects in the United States, you must use NEC-compliant NM-B cable.
- Project Specifications: Always adhere to the specifications outlined by the engineer, architect, or local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ).
- Application Match: Ensure the cable is rated for the specific environment. Both NMD-90 and NM-B are for dry, interior locations only. For damp, wet, or outdoor locations, or for conduits, other cable types (e.g., NMWU, UF-B, THHN/THWN) are required.
Never substitute one for the other based solely on physical similarity. Using a cable not approved for your region can fail inspection, void insurance, and create serious safety hazards.
Choose JZD Cable for Your Reliable Wiring Solutions
Whether your project calls for compliant building wire or specialized cables, JZD Cable is your trusted partner. We manufacture a comprehensive range of high-quality NMD-90 cables for the Canadian market and other international standard wires, ensuring strict adherence to CSA, UL, and other global certifications.
Our cables are engineered for performance, durability, and, above all, safety. We understand that the right wire is the backbone of any safe electrical installation.
Contact JZD Cable today to discuss your project requirements or to request a quote. Let us provide you with the reliable, certified wiring solutions you need to build with confidence.