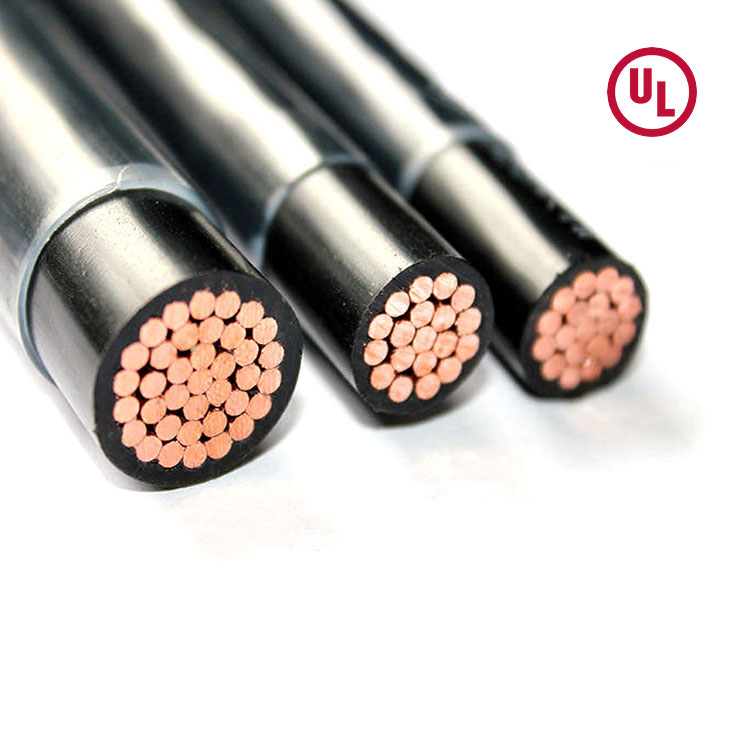
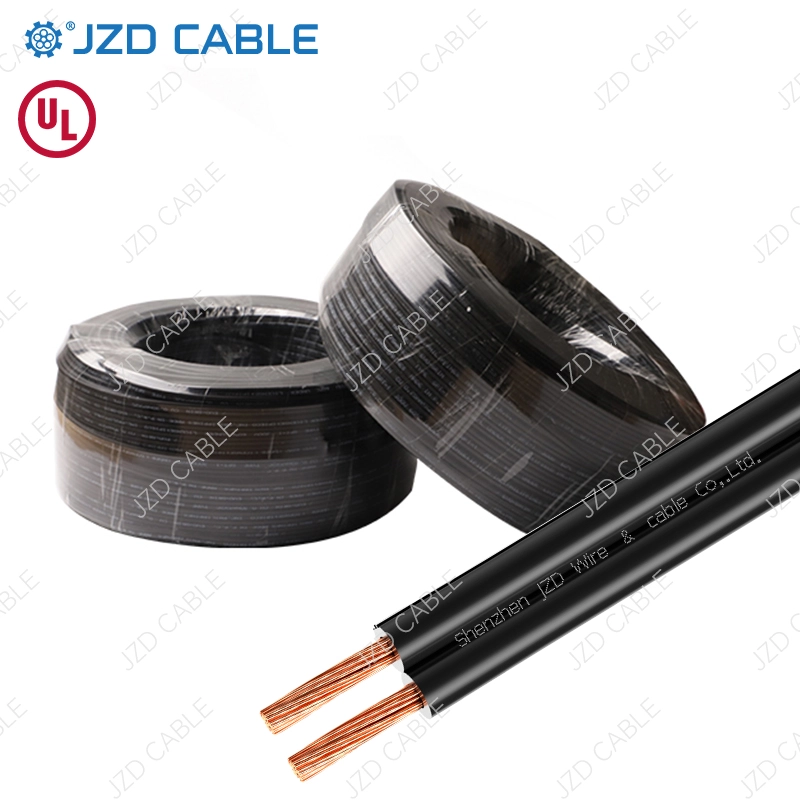
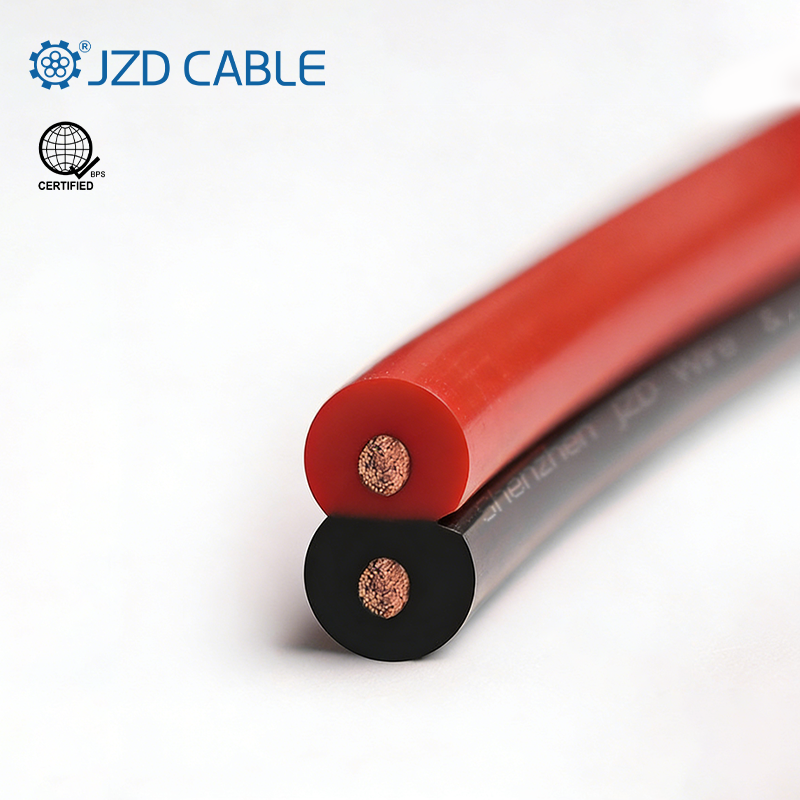
In the world of wires and cables, the Red and Black Parallel Wire (also known as flat parallel cord) is a common and versatile solution. Comprising one red and one black insulated copper conductor extruded side-by-side, its simple design belies its critical role in applications ranging from household appliances to electronics and industrial sectors. Wondering what makes this seemingly simple wire so widely applicable? This article delves into its features, common uses, and a guide to selecting the right cable.
What is Red and Black Parallel Wire?
Red and Black Parallel Wire, also known as flat parallel cord, is a type of unjacketed flexible cable consisting of one red and one black insulated copper wire extruded side by side. This versatile cable is widely used for connecting various portable electrical appliances, instruments, telecommunication equipment, and automation devices.
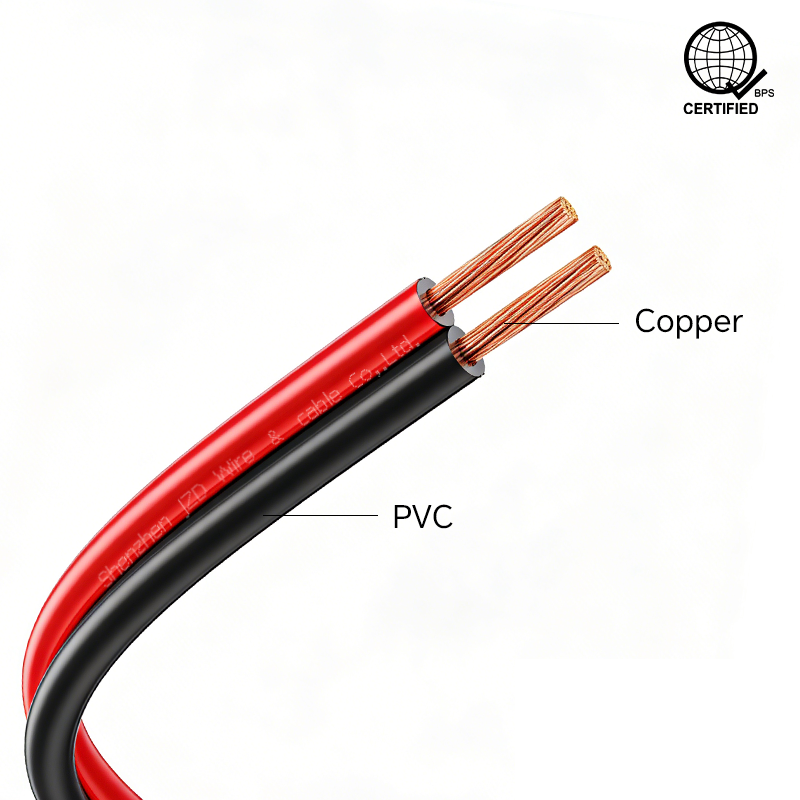
Features of Red and Black Parallel Wire
1. Structure and Appearance
- Unjacketed Design:Features a flat, parallel two-wire structure without an additional outer sheath.
- Color Coding:The red and black insulation allows for easy identification of positive/negative poles or circuit functions.
2. Conductor and Insulation Material
- Conductor:Made of stranded bare copper, offering excellent conductivity and low resistance.
- Insulation:PVC material provides superior insulation, mechanical strength, and aging resistance.
3. Flexibility and Installation Advantages
- The stranded design ensures flexibility, making it ideal for complex wiring environments, especially inside electronic devices or applications requiring frequent movement.
- The flat parallel shape saves space, making it suitable for dense wiring layouts, such as in home renovations or conduit installations.
Common Applications
-
Household Appliance Connections: Used for connecting table lamps, floor lamps, fans, televisions, audio systems, and other small appliances. Its flexibility and color-coding simplify installation.
-
Internal Wiring for Electronic Devices: Widely applied in computers, tablets, and other devices for connecting circuit boards, batteries, and mainboards.
-
Lighting and Control Circuits: Suitable for home lighting, instrument panels, broadcast audio control lines, and fire alarm systems.
-
Industrial and Tool Applications: Ideal for power transmission in small-to-medium pneumatic tools, instruments, and control panels. Suitable for environments with temperatures not lower than -15°C.
Avoid Common Wiring Mistakes
-
Incorrect conductor size or voltage rating. -
Improper installation methods, such as over-bending or compression. -
Ignoring environmental factors like temperature, chemical exposure, or mechanical stress. -
Using low-quality cables to save costs, which may cause safety hazards or premature failure. -
Overlooking certifications like UL, CE, or TUV.
Pro Tips:
- Evaluate environmental conditions, mechanical needs, and electrical requirements.
- Verify certification compliance and ensure the cable meets project-specific parameters.