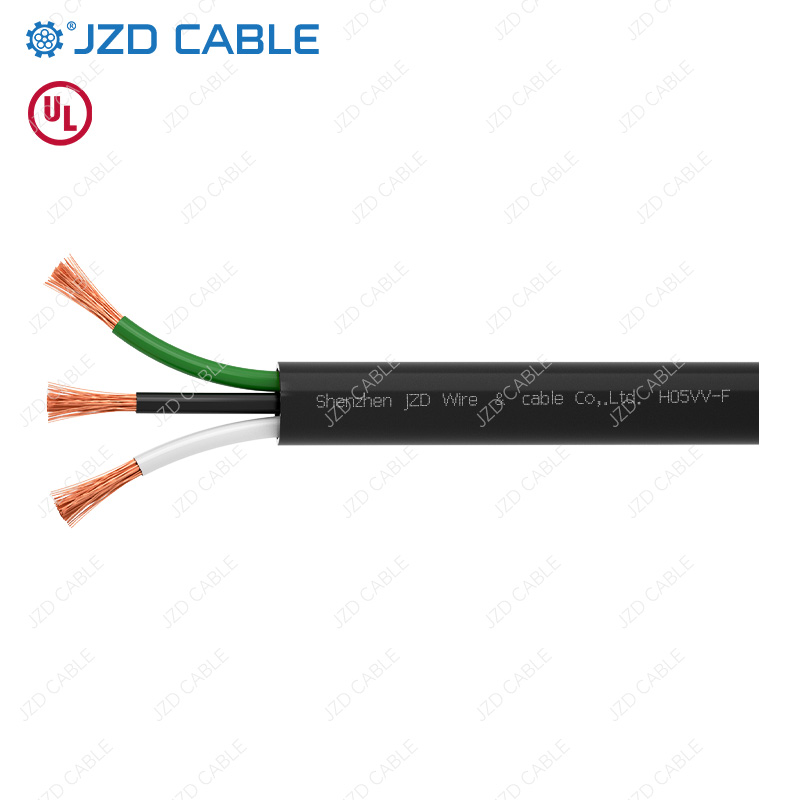
When you need durable, flexible, and safe power delivery for tools, equipment, or temporary power setups, portable power cords are essential. However, navigating the different types – especially common UL standards like STW, SJTW, and SJT – can be confusing. Choosing the right cord ensures safety, longevity, and optimal performance for your specific environment. Let’s break down these popular UL-certified portable cord types, their features, applications, and key differences.
What are STW, SJTW, and SJT Cords?
All three are types of flexible portable power cords certified by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) to rigorous safety standards. They are widely used for construction sites, workshops, industrial applications, entertainment setups, appliances, and general extension cords. Their common features include:
- Flexible Stranded Copper Conductors: Allow for easy handling and coiling/uncoiling.
- Insulated Conductors: Each internal conductor has individual insulation.
- Overall Jacket (Outer Sheath): Provides protection against abrasion, chemicals, and environmental factors (varying by type).
- UL Certification: Guarantees compliance with strict electrical, fire, and mechanical safety requirements for portable cord use.
- Suffix ‘W’: Indicates suitability for outdoor use and resistance to wet conditions, sunlight (UV), weather, and typically oil.
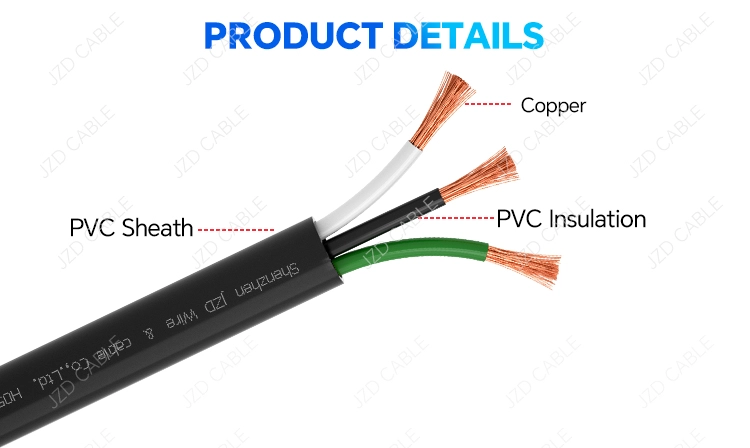
Key Differences Between STW, SJTW, and SJT Portable Cords
The main differences lie in their jacket material, temperature rating, environmental resistance, and resulting applications:
| Feature | STW Cord | SJTW Cord | SJT Cord |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Jacket Material | Thermoset Rubber (e.g., CPE, Neoprene) | Thermoplastic (PVC or Equiv.) | Thermoplastic (PVC or Equiv.) |
| Temperature Rating | -50°C to +90°C (-58°F to 194°F) | -40°C to +90°C (-40°F to 194°F) | -40°C to +90°F (-40°F to 194°F) |
| Outdoor Suitability (Wet Locations) | Excellent | Good | Not Designed For |
| Sunlight (UV) Resistance | Excellent | Good (Often labeled Sun Res) | Poor (Degrades Fast) |
| Oil & Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good (Varies by formulation) | Poor |
| Flexibility in Cold | Excellent (Remains flexible) | Good | Stiffens significantly |
| Typical Applications | Industrial, Outdoor, Extrême Cold, Oil Exposure | General Purpose, Workshops, Construction Sites (Indoor/Outdoor), Tools | Indoor Appliances, Office Equipment, Non-Demanding Indoor Use |
Detailed Look at Each Cord Type
- STW Cord (UL Standard 62)
- Jacket: Made from thermoset rubber (like neoprene or CPE). This is more expensive than thermoplastic but offers superior performance.
- Key Advantages:
- Outstanding resistance to oil, gasoline, ozone, and chemicals.
- Exceptional resistance to sunlight (UV) and weathering, making it truly suitable for permanent outdoor exposure.
- Remains highly flexible down to extremely low temperatures (-50°C / -58°F).
- High abrasion resistance and durability.
- Applications: Heavy industrial environments (factories, refineries, mills), outdoor construction sites exposed to sun and weather, oil fields, marine docks, cold storage freezers, mining, and any demanding application requiring maximum resistance to harsh elements and oils.
- SJTW Cord (UL Standard 62)
- Jacket: Made from tough thermoplastic material (usually PVC or a UV-resistant PVC compound). Look for “SJTW-A” where the ‘A’ indicates sunlight (UV) resistance.
- Key Advantages:
- Designed for both indoor and outdoor use. The ‘W’ suffix explicitly means weather/water-resistant.
- Good resistance to water, sunlight (UV – especially if SJTW-A), and abrasion.
- Generally more resistant to oil than SJT (though not as robust as STW).
- More cost-effective than STW while offering good outdoor durability.
- Remains flexible in moderate cold (down to -40°C / -40°F).
- Applications: Extremely versatile – construction sites, workshops, garages, gardens, power tools, outdoor lighting, temporary event power supply, farm equipment. It’s the “go-to” heavy-duty extension cord and portable power solution for most general industrial/commercial tasks involving outdoor elements.
- SJT Cord (UL Standard 62)
- Jacket: Made from thermoplastic (PVC). Lacks the ‘W’ suffix.
- Important Characteristics:
- Primarily designed for INDOOR USE or temporary protected outdoor use. It is not certified or suitable for prolonged exposure to sunlight (UV), rain, or moisture. UV exposure causes rapid degradation of the PVC jacket.
- Minimal resistance to oil and chemicals.
- Becomes very stiff and brittle at lower temperatures (below freezing).
- Least expensive option of the three.
- Applications: Office environments, connecting indoor appliances (vacuum cleaners, air conditioners – check appliance spec), lamps, non-demanding residential/commercial indoor use. Avoid using SJT as a permanent outdoor extension cord.
How to Choose the Right Cord: STW vs SJTW vs SJT?
- Outdoor or Wet Environment? Choose STW for maximum life and harsh conditions or SJTW for reliable general outdoor duty. Avoid SJT outdoors.
- Exposed to Sunlight (UV)? Choose STW or ensure it’s SJTW-A. SJT will fail quickly.
- Oil, Gasoline, or Chemical Exposure? STW is best. SJTW offers moderate resistance depending on formulation. Avoid SJT.
- Cold Temperatures? STW performs best in extreme cold. SJTW handles moderate cold well. SJT becomes brittle.
- Indoors Only? SJT is sufficient for most applications and cost-effective. SJTW is also safe indoors and provides extra toughness if needed.
- Budget vs. Durability? SJT (Indoor) < SJTW (Indoor/Outdoor Value) < STW (Premium Outdoor/Industrial).
The Critical Importance of UL Certification
Purchasing cords with genuine UL Listed or UL Certified markings is non-negotiable. This certification means:
- The cord meets stringent safety standards for electrical insulation, fire resistance, and mechanical strength.
- The materials and construction are verified for their claimed ratings (voltage, temperature, resistance).
- It undergoes regular UL audits to ensure continued compliance.
- Using non-UL certified cords risks fire, electric shock, and equipment damage.

In summary: While STW, SJTW, and SJT cords look similar at a glance, their jacket materials and certifications dictate vastly different uses. STW is the heavy-duty champion for extreme environments, oil, and cold. SJTW (especially SJTW-A) is the versatile workhorse for reliable indoor/outdoor industrial and commercial power. SJT is strictly an economical choice for general indoor use only. Always prioritize UL certification for safety and verify the specific ratings printed on the cord jacket. Choosing the correct UL-certified portable power cord ensures safety, performance, and long-term cost savings.
Need UL-Certified STW, SJTW, or SJT Portable Power Cables? Explore JZD Cable’s range of durable and reliable solutions today! Link to STW /SJTW /SJT Product Page or Contact Us for expert guidance.