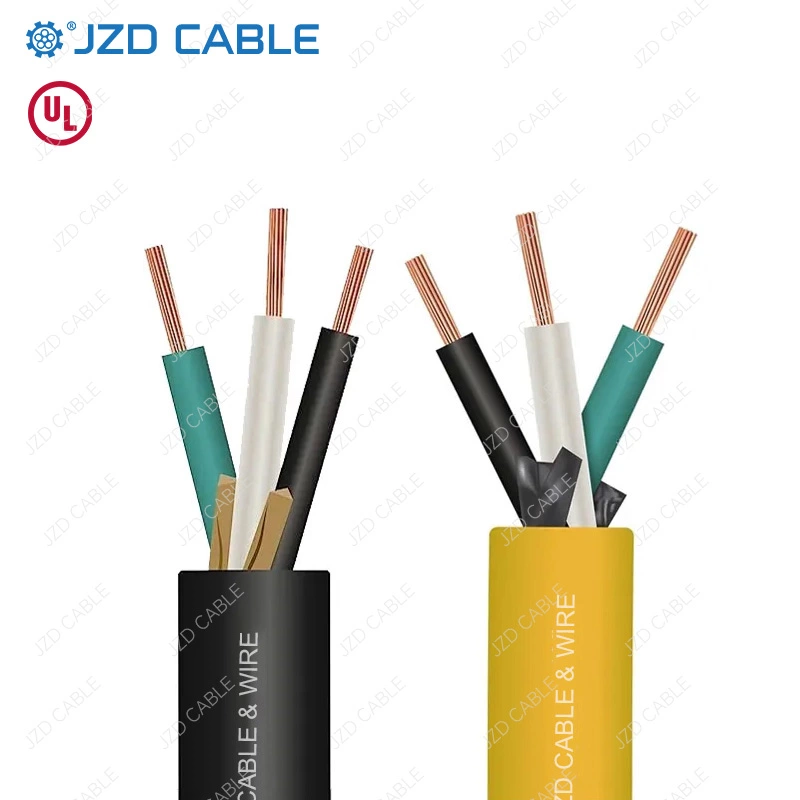
Selecting the right cable for demanding environments exposed to oil, moisture, and harsh weather is critical across industrial, construction, and even residential applications. SOOW/SJOOW cables stand out as a benchmark for durability, renowned for their exceptional flexibility and robust environmental resistance. But what do the letters in their names truly signify? This guide delves into the features, applications, and common selection pitfalls of these versatile workhorse cables, empowering you to make an informed decision for your next project.
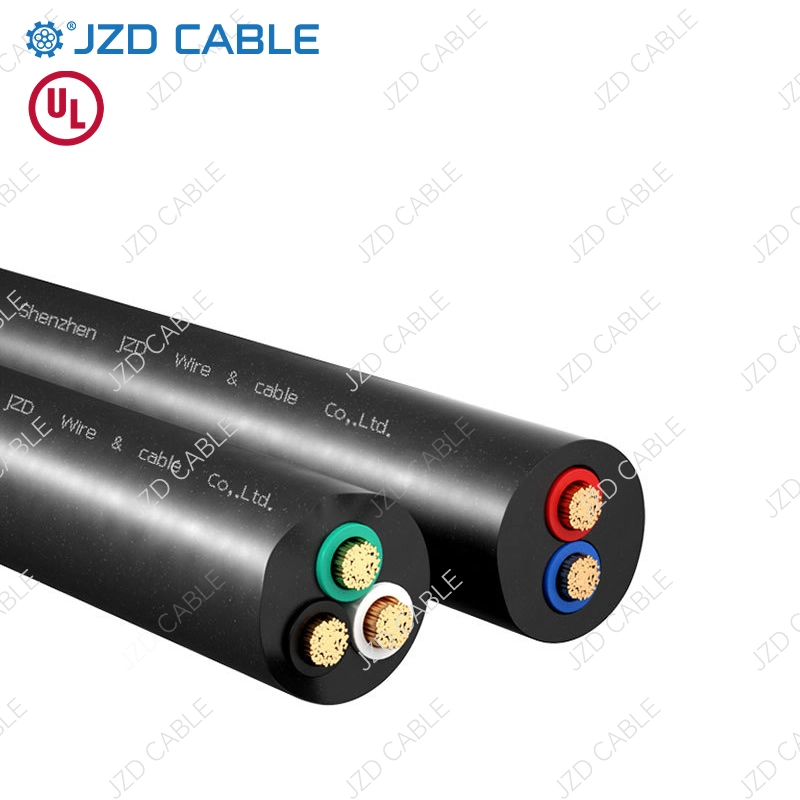
What is SOOW/SJOOW Cable?
- S: Cables starting with “S” have a rated voltage of 600V.
- SJ: Known as “Junior Jacket,” these cables have a rated voltage of 300V.
- O: Oil-resistant insulation.
- OO: Additional “O” indicates oil-resistant insulation and outer sheath.
- W: Weather-resistant and waterproof.
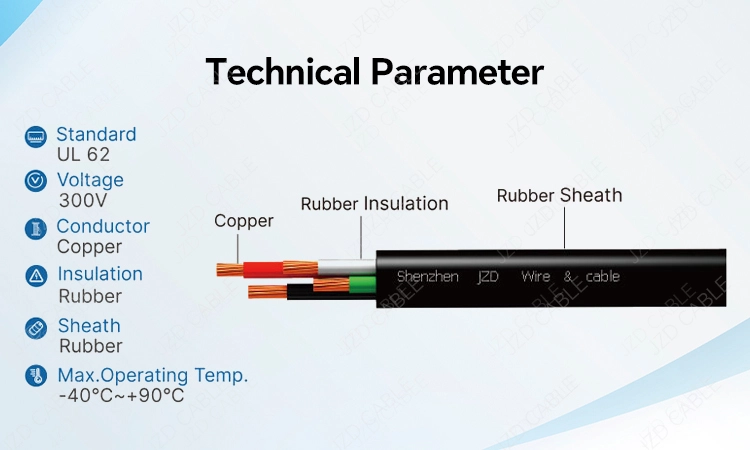
Key Features of SOOW/SJOOW Cable
-
Oil Resistance: Withstands oily environments without degradation. -
Flame Retardancy: Effectively prevents fire spread. -
Abrasion Resistance: The outer sheath resists wear from external forces. -
Weather Resistance: Performs reliably in harsh climates. -
Flexibility: Easy to install and route, even in tight spaces.

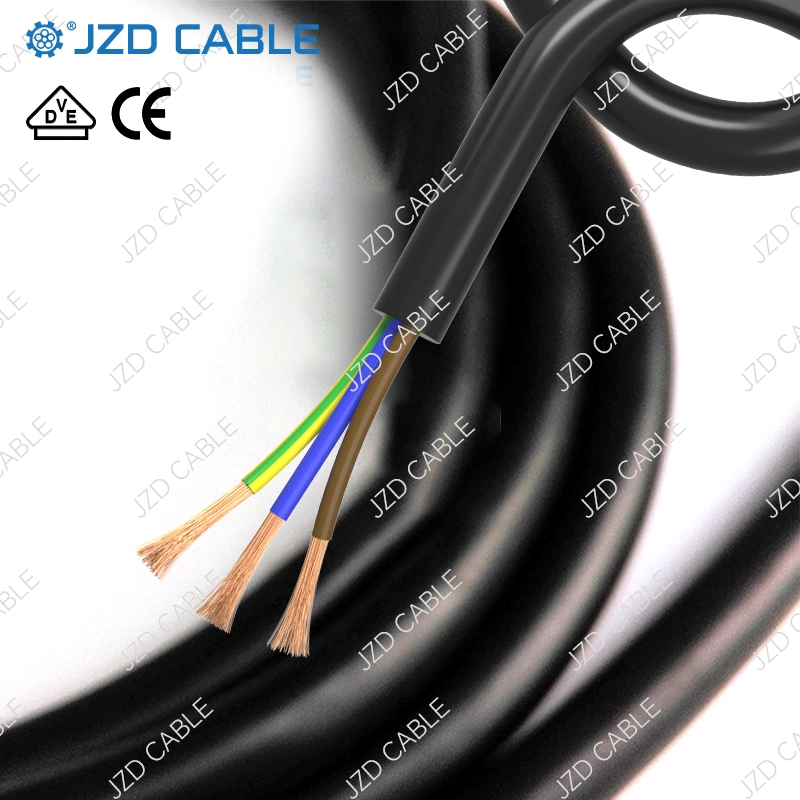
Typical Applications
- Industrial Machinery: Cranes, machine tools, port equipment, submersible pumps.
- Mobile Equipment: Electric tools, battery chargers, portable lighting.
- Household Appliances: Kitchen devices, outdoor electronics.
- Special Environments: Chemical plants, petroleum facilities, marine settings.

Common Mistakes in Selecting SOOW/SJOOW Cable
-
Incorrect Conductor Size or Voltage Rating: Undersized cables can overheat, causing voltage drops or failure. -
Improper Installation: Excessive bending or compression damages insulation, leading to short circuits. -
Ignoring Environmental Factors: Temperature, chemicals, and mechanical stress impact cable longevity. -
Choosing Low-Quality Cables: Cheap options may save costs initially but risk failures, safety hazards, and frequent replacements. -
Overlooking Certifications: Non-compliance with UL, CE, or TUV standards can result in regulatory issues.








