Understanding the right cable for your specific application is crucial for safety, performance, and durability. One type of wire frequently encountered, especially in connecting devices, is the Lead Wire. But what exactly is it, where is it used, and how does it differ from “normal” wire? Let’s delve into the specifics.
What is a Lead Wire?
A lead wire, also commonly called an appliance wire or a hook-up wire, is an insulated single conductor or a pair/trio of conductors designed to provide a flexible, reliable electrical connection between a power source or controller and a specific device or component. Unlike wire meant for permanent building wiring within walls, lead wires are typically used for the final connection to an appliance, motor, sensor, switch, or other piece of equipment.
Key Characteristics of Lead Wires:
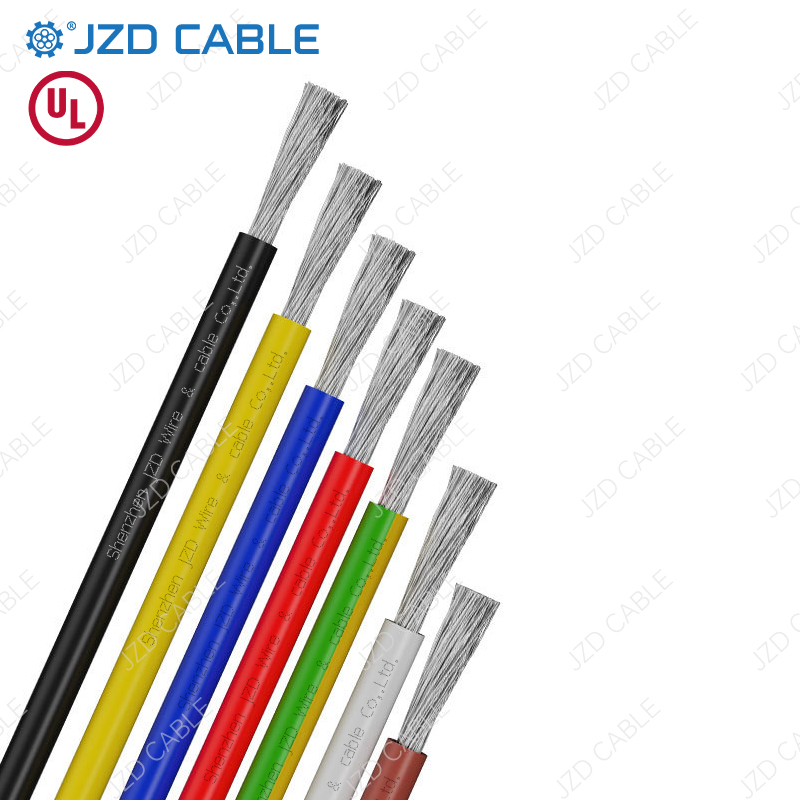
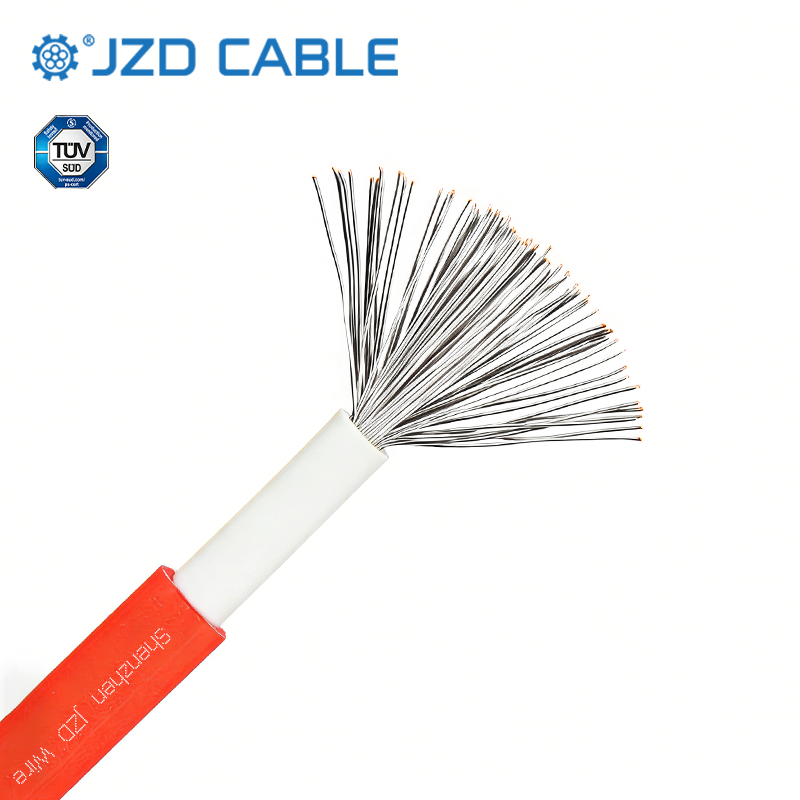
- Flexibility: Often constructed with stranded conductors (multiple fine wires bundled together) for repeated bending and movement without breaking.
- Durable Insulation: Features robust insulation designed to withstand the environmental conditions of its application (e.g., moisture, heat, oils, abrasion). Common insulation materials include PVC, Silicone Rubber, Teflon (PTFE), and Rubber.
- Termination Ready: Lead wires frequently come pre-terminated with connectors (like spade terminals, ring terminals, or plugs) for easy and secure attachment to devices, though they can also be supplied on reels for custom termination.
- Voltage Rating: Designed for specific voltage ranges, commonly UL/CSA rated for 300V, 600V, or higher depending on application requirements.
- Sizing: Available in various American Wire Gauge (AWG) sizes, with 18 AWG, 16 AWG, and 14 AWG being common for appliance and light industrial uses.
Common Applications of Lead Wires
Lead wires are ubiquitous in environments where power needs to be reliably and safely delivered to a specific point of use. You’ll find them in:
- Household Appliances: Connecting motors in blenders, vacuums, washing machines, dryers, and refrigerators; internal wiring for ovens, toasters, and microwaves.
- Industrial Equipment & Machinery: Connecting sensors, controls, solenoids, small motors, indicator lights, and switches on factory floors.
- Medical Devices: Powering and connecting components in diagnostic equipment, patient monitors, and therapeutic devices (requiring specialized biocompatible or highly flexible silicone insulation).
- Automotive Applications: Wiring for interior lights, sensors, audio systems, and non-engine compartment accessories.
- Consumer Electronics: Power cords for computers, monitors, and peripherals; internal connections in audio/video equipment.
- Electrical Enclosures: Used for internal wiring within control panels, junction boxes, and power supplies.
- Test & Measurement Equipment: Connections for probes, meters, and oscilloscopes.

What is the Difference Between Lead Wire, Hookup Wire, and Building Wire?
The terms “lead wire” and “hookup wire” are often used interchangeably, but subtle differences exist. Here’s a clear comparison of Lead Wire, Hookup Wire, and Building Wire:
1. Lead Wire
- Purpose: Flexible connection to devices/appliances (e.g., motors, sensors, switches).
- Construction: Stranded conductors + insulation (PVC, silicone, Teflon).
- Termination: Pre-terminated with connectors (spade/ring terminals).
- Flexibility: High (optimized for repeated bending).
- Applications: Power cords for appliances, industrial machinery, medical devices.
2. Hookup Wire
- Purpose: Internal electrical connections (e.g., circuit boards, control panels).
- Construction: Stranded/solid conductors + thin insulation (PVC, PTFE).
- Termination: Raw ends (requires manual termination).
- Flexibility: Moderate (suited for static/low-movement installations).
- Applications: Electronics, automotive interiors, control panel wiring.
3. Building Wire (e.g., THHN/Romex)
- Purpose: Permanent structural wiring (walls, conduits, junction boxes).
- Construction: Solid/stiff conductors + thick insulation.
- Termination: Spliced or screwed into electrical boxes.
- Flexibility: Low (not designed for movement).
- Applications: Residential wiring, branch circuits, infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lead Wire | Hookup Wire | Building Wire |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Device/Appliance Connections | Internal Electronics | Permanent Structural Wiring |
| Conductor | Stranded (flexible) | Stranded/Solid | Solid/Stranded (stiff) |
| Termination | Pre-terminated | Raw Ends (DIY termination) | Spliced/Screwed |
| Insulation | Thick, environment-resistant | Thin (PVC/PTFE) | Robust (THHN/NM-B) |
| Flexibility | ★★★ (High) | ★★☆ (Moderate) | ★☆☆ (Low) |
| Examples | Appliance cords, sensors | PCB wiring, control panels | Romex®, THHN cable |
Why Choose Quality Lead Wires from JZD Cable?
Incorrect or substandard wiring compromises safety and equipment longevity. JZD Cable supplies lead wires crafted with precision:
- Certified Quality: Meeting UL, CSA, RoHS, and other relevant international safety standards.
- Material Excellence: High-quality copper conductors and durable insulation materials selected for performance in demanding environments.
- Flexibility & Durability: Stranding patterns and insulation formulations optimized for reliable flex life and resistance to heat, chemicals, and abrasion.
- Customization: Capabilities include custom lengths, stripping, color coding, and termination with various connectors.
- Performance Assurance: Reliable conductivity and consistent electrical characteristics.

Conclusion
Hookup wire is a lead wire used in many different low-current (and low-voltage) electronic applications. So, when you hear the term hookup wire, you know someone is referring to a type of lead wire.Building wires, in contrast, serve rigid installations. At JZD Cable, our lead wires and hookup wires undergo stringent UL/CSA testing for reliability across industries.
Lead wires are the essential, flexible links that bring power and signals to the countless devices we rely on daily. Understanding their unique characteristics – flexibility, termination readiness, and specific insulation requirements – is key to selecting the right wire for the job.
Need high-performance lead wires for your application? Browse JZD Cable’s range of Lead Wires or Contact Us today for expert advice and custom solutions!